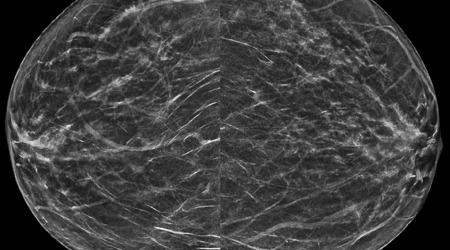
Breast Imaging
While breast cancer occurs in both males and females, women account for approximately 99% of all breast cancers. Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women, after skin cancer. Radiology Waukesha uses tomosynthesis, also known as 3-D mammography, for routine screening examinations. Early detection of breast cancer decreases breast cancer mortality; therefore, the American College of Radiology recommends annual mammographic screening beginning at age 40 for women at average risk for breast cancer. Radiology Waukesha radiologists screen mammography patients and refer those with higher-than-average risk of breast cancer to the High Risk Breast Clinic. These higher-than-average risk patients benefit from starting mammographic screening younger than 40, and receiving supplemental screening such as breast MRI.
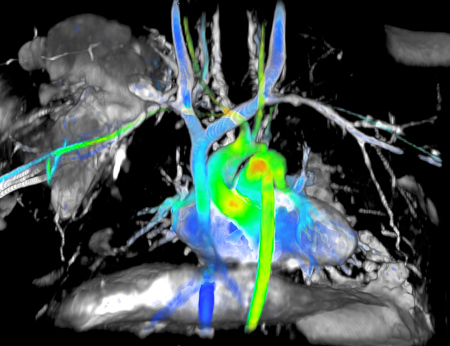
Cardiac Imaging
Radiology Waukesha stands at the forefront of non-invasive cardiac imaging with extensive experience and expertise in coronary CT angiography, cardiac nuclear medicine, and cardiac MRI. Cardiac MRI acquires exceptionally clear pictures and dynamic motion cine “videos” to enable the evaluation of the function, morphology, and flow dynamics of the heart. As a highly specialized tool, Cardiac MRI is typically only available at large academic hospitals. Radiology Waukesha has provided this high-quality service to the community for over 15 years, since the technology was first available.
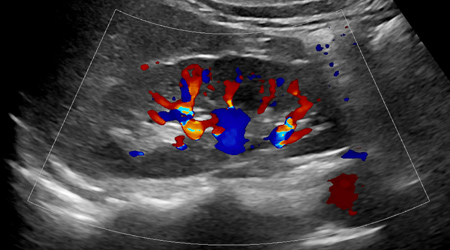
Ultrasound
Radiology Waukesha offers comprehensive diagnostic ultrasound services including imaging of the abdominal area (including pancreas, liver, gallbladder, spleen, kidneys and bladder), abdominal aorta (including abdominal aortic aneurysm screening), breast, female pelvis (including first trimester pregnancy), lymph nodes, neonatal head, muscles, skin, soft tissue, testicles, thyroid, and veins. The techniques routinely used include gray scale, color and power Doppler, and shear wave elastography. In addition, Radiology Waukesha’s radiologists perform a wide variety of ultrasound-guided procedures, including solid-organ biopsy and sonohysterography.
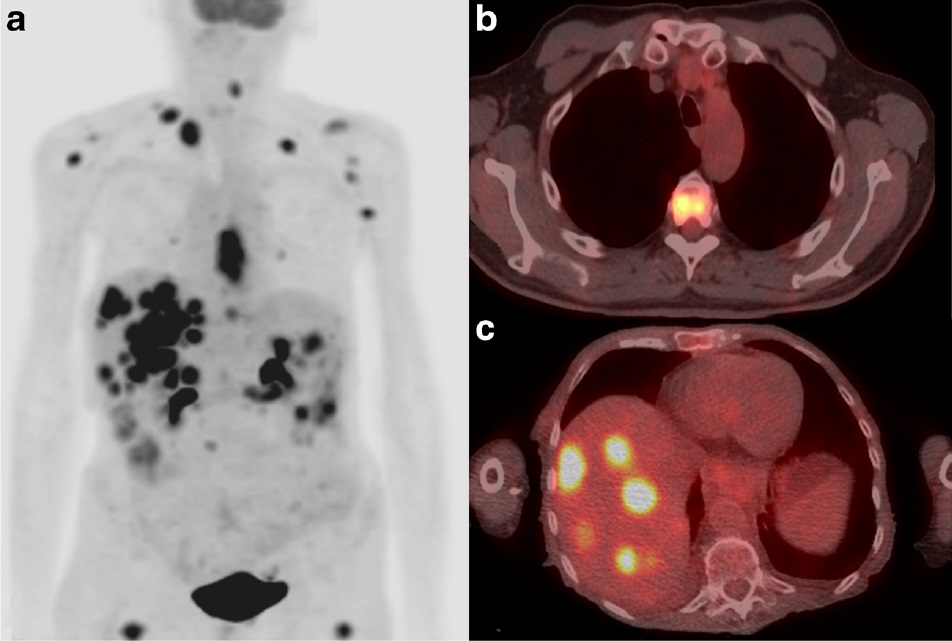
CT
Computed tomography (CT) uses x-ray beams which rapidly rotate around a patient to speedily acquire two-dimensional images which can be processed into three-dimensional images for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The applications of CT are broad, and examinations are performed for every body part, from head to toe. CT of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis is routinely performed for the diagnosis and surveillance of cancer. Radiology Waukesha serves two Primary Stroke Centers, sites which guarantee that patients with a suspected stroke receive an expeditious head CT with immediate verbal communication of the findings. In addition, Advanced RAPID CT perfusion software is used to view detailed images of the brain clearly and quickly. Intravenous contrast given in CT angiography allows for the evaluation of blood vessels in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, arms, and legs.
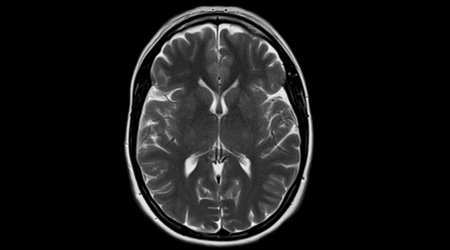
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is unique in that it uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce images of the body. Commonly imaged body parts include the head, breast, heart, abdomen, pelvis, uterus and ovaries, prostate, shoulder, spine, hip, and knee. Multiparametric prostate MRI is performed to evaluate suspected prostate, cancer according to the standards of the Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS). MRI-guided breast biopsy is performed by Radiology Waukesha’s experienced breast imaging radiologists. Patients with metal inside their body are individually screened for safety prior to entering the magnetic field near the MRI scanner.
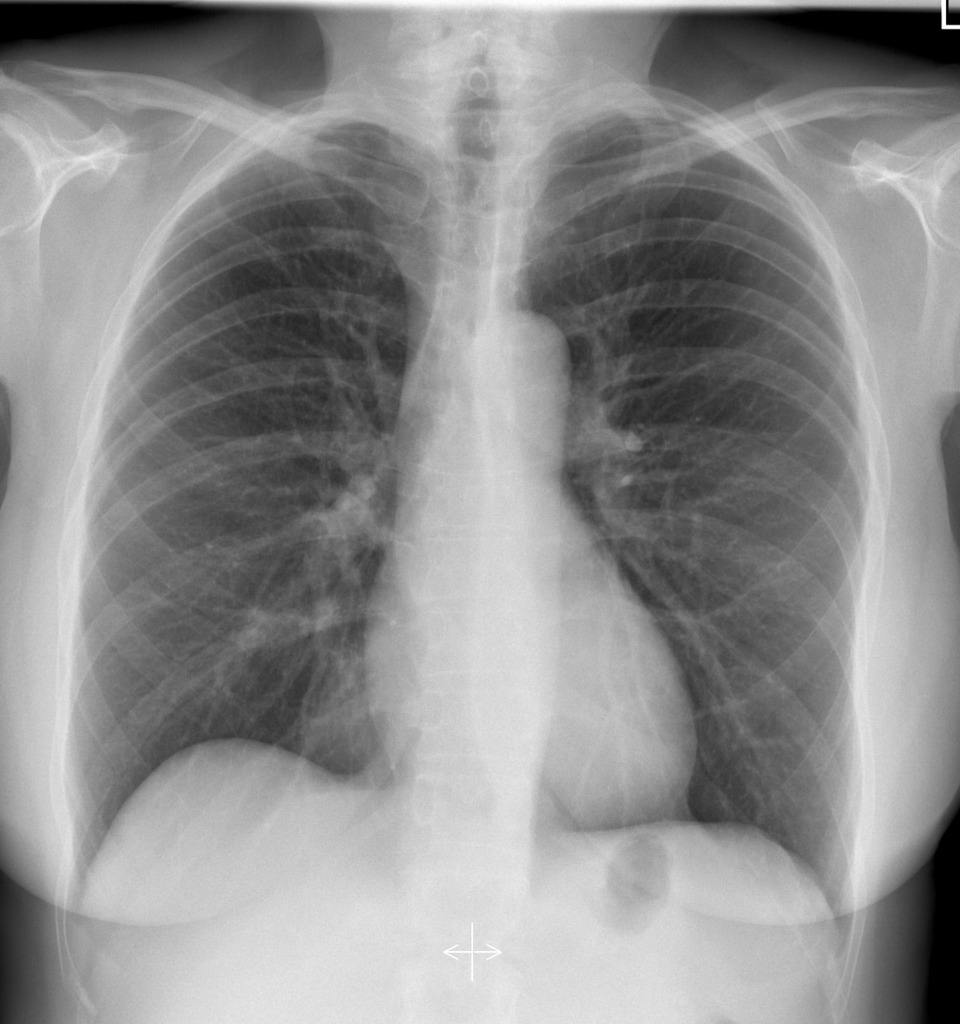
X-Ray
Radiographs, or x-rays, use small doses of ionizing radiation to quickly produce a detailed static two-dimensional image. Chest x-rays are commonly acquired to evaluate for cardiac disease, respiratory disease, infectious disease, metastatic disease, and to evaluate the position of endotracheal tubes and central venous catheters in critically ill patients. Chest x-rays are anecdotally considered the most frequent radiologic examination globally. Radiographs are also commonly acquired of the bones to evaluate for fracture or dislocation, and of the abdomen to evaluate for bowel obstruction or kidney stones. Dynamic x-ray images, referred to as fluoroscopy, are used to guide a wide range of non-invasive and invasive procedures, such as hip and shoulder injections, hysterosalpingography, esophagram, barium enema, and myelogram.
